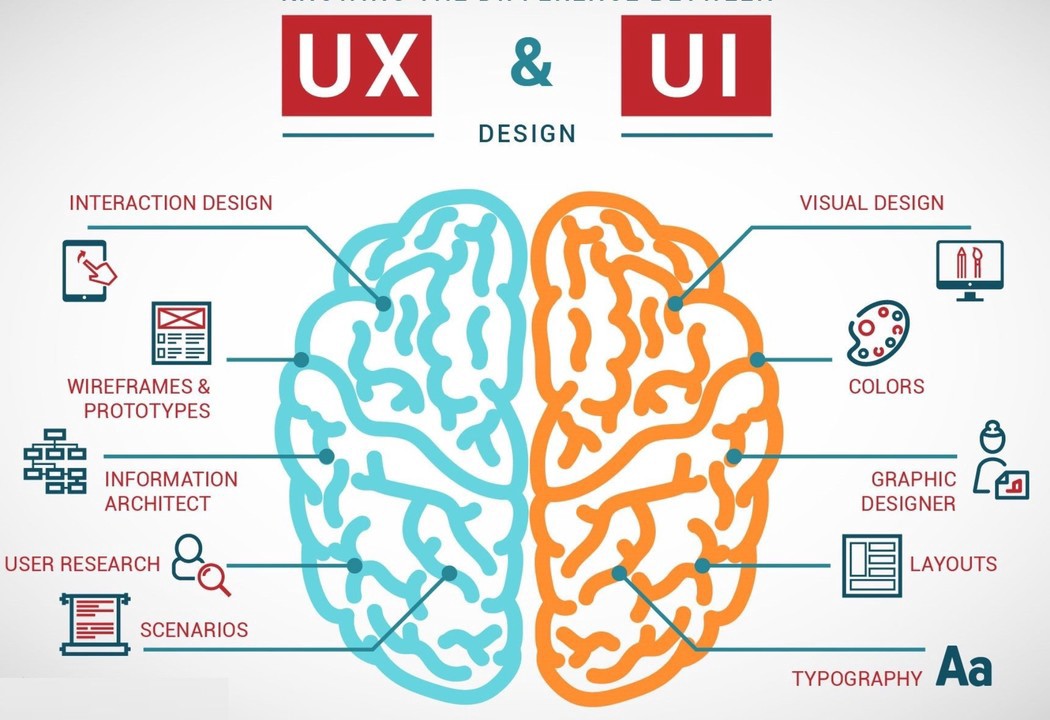
What is UX / UI design? What does a UX / UI designer do? What’s The difference between them?
User Experience (UX) Design and User Interface (UI) Design are the two essential pillars of website creation. If either one is neglected, the website will suffer a bad time. So if you’re planning to create a new website or develop an existing one, you need to know about UX Design and UI Design:
What is UX Design?
User Experience (UX) Design enhances user satisfaction by improving the usability, accessibility, and pleasure provided in the interaction between the user and the product.
The main focus of “User Experience Design” is to create a simple and easy-to-use interface that makes an application easier to use. This includes making sure that it is easy to navigate, easy to understand, and quick enough so that users don’t get frustrated while using it.
- For example, if you were designing a website for a company called “My Business,” you would want your website to be as simple and easy as possible for people unfamiliar with computers or websites. You would also like your website to look professional so that people visiting your site would take you seriously.
What is UI Design?
User Interface (UI) Design refers to creating computer interfaces, such as windows and buttons, on a screen. The term “User Interface Design” generally refers to a specific aspect of a system’s software or hardware, rather than the entire system itself.
The User Interface is what people see and interact with when they use a device. It consists of all the screens, buttons, icons, and text that allow users to type documents or get directions on their smartphones.
Users need to navigate an interface easily to accomplish their tasks without frustration. A good User Experience requires a compelling interface that lets users quickly find what they’re looking for without being distracted by unnecessary features.
What does a UX/UI Designer Do?
UX/UI design combines User Experience and User Interface design. User Experience (UX) refers to how a person feels about using a product, system, or service. It includes utility, ease of use, and emotional satisfaction. User Interface (UI) is how a person interacts with a product, system, or service through navigation, graphics, and feedback.
A UX/UI designer is responsible for creating an effective User Experience (UX) and User Interface (UI) for applications, websites, mobile devices, and other products that customers or employees use. This role aims to create an engaging experience for users, so they will enjoy using the product and provide positive feedback.
However, there are a few general responsibilities that a UX/UI designer must fulfil. Here is a brief outline of the typical tasks designers perform at work:
-
Conducting User Research
Research is the first step in the UX design process. It can take various forms, including desk research and field research. The objective is to obtain a complete image of the intended audience for the product or service.
-
Developing User Personas
Based on user research, UX/UI designers develop user personas that explore the tasks each persona wishes to do and why in greater detail. A typical persona consists of demographic information, details on preferences, habits, likes, dislikes, and ties to trends.
-
Development of the Information Architecture
Next, designers consider the type of information featured in the final product or promotional materials. They analyse how vital information will be arranged throughout the website or application. This is known as information architecture, and its creation requires determining the most logical content layout and organization.
-
Developing User Flows and Wireframes
UX/UI designers utilize various methods to map the user’s pathway through a product. Examples include user flows and wireframes.
User flows are simple flowcharts depicting the user’s path when interacting with a product, beginning with the entry point and finishing with the final engagement.
-
User Testing and Prototyping
What is a prototype exactly? It is a scaled-down version of the product that allows teams to test their designs before submitting them to development.
Before investing in the final product, firms can detect any design issues by testing prototypes on actual users.
-
Involvement in the Development
The designers play a vital role even after the product has entered the development phase. They attend sprint meetings, oversee product development to ensure the team avoids feature creep, and make minor design adjustments. In addition, they engage in the design of new release features and assess user feedback.
-
Visual Design
Some UX designers also focus on visual design, where they take on the responsibilities of a UX/UI designer. Consequently, they are responsible for choosing the final artwork, colour schemes, icons, and typography.
Differences Between UX and UI Design
User Experience Design and User Interface Design have a lot in common. Both disciplines strive to make products easy, intuitive, and enjoyable. Both require a deep understanding of users’ needs and preferences. And both are integral components of modern web development projects.
But there are also some key differences between UX design and UI design. These differences are given below:
-
Look vs. Feel
UX and UI design play similar but distinct functions in creating a product. UI design is concerned with the appearance of a product, including the visual and interactive features that contribute to a positive User Experience. UX design, on the other hand, concentrates on the overall feel of the product or service and the elements that will contribute to a meaningful, relevant User Experience.
-
Design vs. Prototyping
UX and UI designers may collaborate on the same project, but have distinct responsibilities and objectives. UX designers frequently build wireframes and testable prototypes that are the foundation for a website or service’s user flow. In contrast, UI designer’s complete products and designs that encourage user engagement.
-
High-Level vs. Details
Another distinction between UI and UX designers is the level of attention to detail in their respective work. Individual pages, buttons, and interactions are refined and functionally tested by UI designers. UX designers take a broader perspective on a product or service, ensuring that the overall user flow of a website, service, or application is completely realized and consistent.
Final Thoughts
The terms User Experience Design, or UXD, and User Interface Design, or UID, are often seen as interchangeable. They both deal with a user’s interaction with a product, service, and application. However, there are distinct differences between these two areas of design. It is essential to understand them to understand the best methodology for dealing with UI and UX Design.